EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT MICROCHIPPING YOUR PET

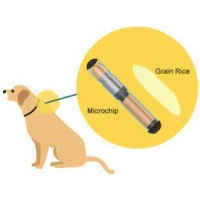
WHAT IS MICROCHIP?
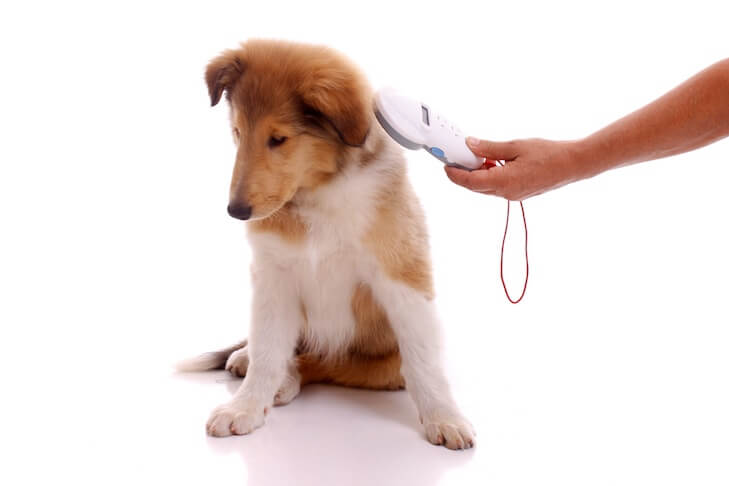
A microchip is a radio-frequency identification transponder that carries a unique identification number and is roughly the size of a grain of rice. When the microchip is scanned by a vet, it transmits the ID number. There’s no battery, no power required, and no moving parts. The microchip is injected under the loose skin between your dog’s shoulder blades and can be done in vet hospital. It’s no more invasive than a vaccination.

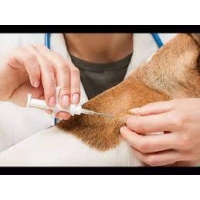
HOW MICROCHIP IS IMPLANTED?
Before insertion, the sterile microchip is scanned in the package to confirm that the identification code of the transponder is the same as that shown on the package bar code label. The needle containing the microchip is loaded into the application gun or syringe, and your dog is positioned for the injection. For dogs, the standard site for microchip placement is in the subcutaneous tissue along the dorsal midline (the spine) between the dog's shoulder blades. For correct placement, your dog should be either standing or lying on his stomach. Some of the loose skin between the shoulder blades is gently pulled up, and the needle is quickly inserted. The applicator trigger is squeezed, injecting the microchip into the tissue. After insertion, the dog is scanned to ensure that the chip is reading properly.

HOW MICROCHIP WORKS?
A microchip’s sole function is to store a unique ID number, it differs from a Global Positioning System. When a microchip scanner is passed over the skin of a microchipped pet, the implanted microchip emits an RF (radio frequency) signal. The scanner reads the microchip’s unique ID code.

BENEFITS OF MICROCHIPING?
# Identification and reunion: When pet is lost or separated from pet parents, dogs microchip is scanned and owner’s information will be collected to reunite.
# International travel: Microchipping is one of the main requirements for pet’s international travel, many countries made it compulsory to have microchip with updated detailed before entry.
# To certify a dog’s pedigree: Microchipping is necessary to register with any kennel club to certify pet’s pedigree.
To take a pet insurance, microchipping is compulsory.
DISADVANTAGES OF MICROCHIPPING?
# Migration of microchip from its original implantation site
# Failure of microchip, infection/ swelling
Is microchip substitute for GPS?
GPS devices and microchips aren’t substitutes for each other; they’re complementary, and each is useful to locating a lost dog in different ways. A GPS may tell you where your dog is, but it can’t provide your contact information to those nearby that would help return him home. It also requires batteries and can be lost, like a collar or tags. Microchips, because they’re inserted into a dog’s skin, are permanent. While they can’t guide you to your dog’s location, they provide a way for you to be contacted.
Conclusion: Microchipping is a fast, safe and simple non painful procedure which will be done at veterinary hospitals for any domestic pet/animals.

Courtesy : Dr.Roja Basanagoud Patil, Cessna Lifeline Veterinary Hospital, Electronic city,Bengaluru.